Leave Your Message
Choosing the right Hydraulic Control Valve is crucial for the efficiency and performance of any hydraulic system. With a wide variety of options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which valve best suits your specific needs. A Hydraulic Control Valve plays a pivotal role in regulating the flow and pressure within hydraulic circuits, thereby influencing the overall functionality and responsiveness of the machinery it governs.
When selecting a Hydraulic Control Valve, several factors come into play, including the type of system, the required flow rates, and the desired pressure settings. Understanding the operational environment and specific application requirements is essential for making an informed decision. This introduction sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of key considerations and factors involved in choosing the ideal Hydraulic Control Valve for your system, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your hydraulic applications.

Hydraulic control valves are essential components in hydraulic systems, serving as the regulators of fluid flow and pressure. They play a critical role in directing hydraulic fluid to various parts of the machinery, ensuring that the system operates efficiently and effectively. Understanding the different types of hydraulic control valves—such as proportional, directional, and flow control valves—is key to selecting the right component for your application's specific needs. Each type of valve has unique functions and applications, which can dramatically affect the overall operation of your hydraulic system.
The applications of hydraulic control valves extend across various industries, including construction, manufacturing, and agriculture. These valves can manage numerous tasks, from controlling the speed of hydraulic cylinders to ensuring precise movement in automated machinery. For instance, in agricultural equipment, hydraulic control valves allow for the smooth operation of tilling and plowing attachments, enhancing productivity and effectiveness. By choosing the appropriate valve based on factors like flow rate, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions, one can optimize system performance and achieve desired outcomes in both industrial and mobile applications.
When selecting a hydraulic control valve for your system, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One of the primary considerations is the valve type—essentially, whether you need a directional control valve, pressure control valve, or flow control valve. According to a report by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 30-40% of hydraulic system failures stem from inadequate valve selection or malfunction, highlighting the critical nature of making an informed choice.
Another essential factor is the operating pressure and flow rate specifications of your system. The American Hydraulic Association (AHA) points out that valves must align with the maximum pressure ratings to prevent catastrophic failures, which can severely disrupt operations. Additionally, the required flow rate will determine the size and design of the valve, impacting the system's overall efficiency. Using a well-calibrated valve can enhance energy efficiency by up to 20%, reducing operational costs and prolonging equipment lifespan.
Lastly, material compatibility and environmental conditions cannot be overlooked. Valves exposed to high temperatures or corrosive substances require robust materials to withstand wear and tear, as indicated in a recent study published in the Journal of Hydraulic Engineering. The wrong material choice could lead to leaks or field failures, causing significant downtime. Understanding these critical factors allows for a more strategic approach to selecting the right hydraulic control valve, thereby improving system performance and longevity.

When selecting the right hydraulic control valve for your system, it's essential to understand the various types of valves available and their functions. Hydraulic control valves can be broadly categorized into several types, including directional control valves, pressure control valves, and flow control valves. Directional control valves manage the path of hydraulic fluid, enabling or blocking flow in different directions. Pressure control valves maintain the pressure within a hydraulic system, preventing potential damage from overpressure. Flow control valves regulate the flow rate, ensuring that hydraulic actuators receive the appropriate velocity for optimal performance.
According to industry reports, improper selection of hydraulic control valves can lead to a 20% reduction in system efficiency, emphasizing the importance of making informed choices. When selecting valves, consider their specific applications, the required pressure and flow rates, and the operational environment. For instance, systems exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive conditions may require specialized valves designed to withstand such environments.
Tips for choosing the right hydraulic control valve include evaluating the space constraints of your system and ensuring compatibility with existing components. Additionally, always consult technical specifications and performance curves before making a selection. Understanding the interplay of these factors can significantly enhance your system’s reliability and efficiency, enabling smoother operations and reduced maintenance costs.
When it comes to selecting the right hydraulic control valve, evaluating system requirements is pivotal. Begin by assessing the specific needs of your hydraulic system, which includes analyzing the type of fluid, operating pressure, and temperature ranges. Understanding the flow rates required for various applications will help determine the size and capacity of the valve needed. It's essential to consider the performance characteristics, such as response time and control accuracy, as these will directly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the hydraulic system.
Additionally, it is important to factor in environmental conditions where the valve will be installed. This includes considering exposure to elements such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures that may affect the valve's operation. Compatibility with existing components in the system is another critical aspect to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance. Evaluating these system requirements not only aids in selecting the most suitable valve but also contributes to the longevity and reliability of the entire hydraulic system. Taking the time to thoroughly understand these factors will lead to more informed decisions and ultimately enhance system productivity.
| Valve Type | Flow Rate (GPM) | Pressure Rating (PSI) | Operating Temperature (°F) | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directional Control Valve | 5 - 100 | 1500 - 3000 | -20 to 200 | Construction, Manufacturing |
| Pressure Control Valve | 1 - 50 | 1000 - 5000 | -20 to 212 | Agriculture, Mining |
| Flow Control Valve | 2 - 80 | 500 - 3000 | -4 to 150 | Automotive, Aerospace |
| Check Valve | 0 - 30 | 500 - 1500 | -20 to 180 | Water Systems, Oil & Gas |

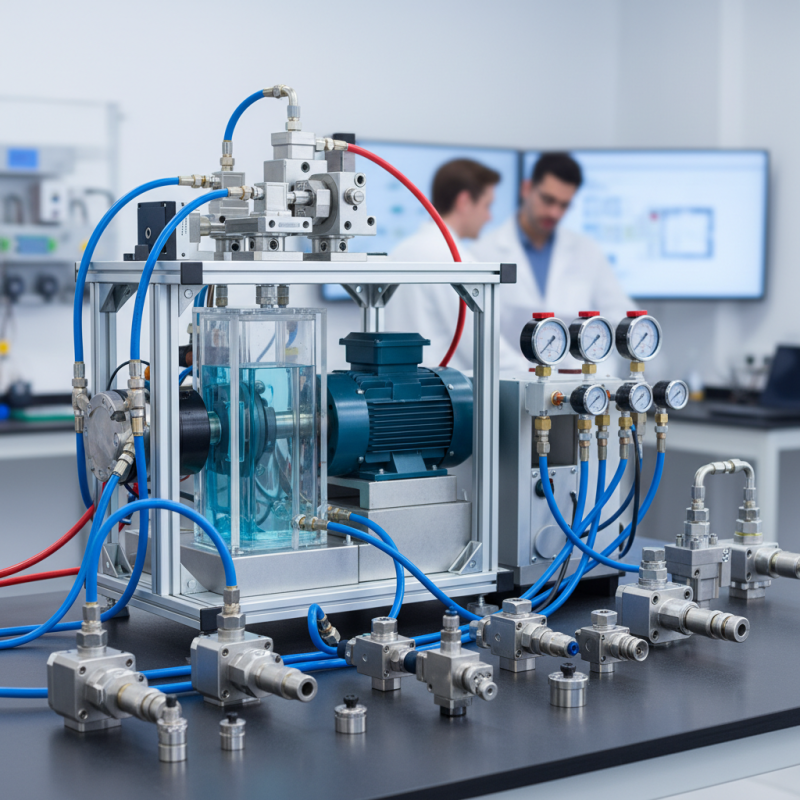
Proper installation and maintenance of hydraulic control valves are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your system. When installing a control valve, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding orientation and mounting. Pay special attention to the flow direction marked on the valve, and ensure all connections are secure to prevent leaks. Using the correct tools and fittings can also help alleviate potential stress on the valve body, which may lead to premature failure. Additionally, implementing adequate filtration systems can protect the valve from particulate contamination.
Regular maintenance is equally important for sustaining valve efficiency. Routine inspections should focus on checking for signs of wear, leaks, and corrosion. It's advisable to clean the valve regularly and replace any worn seals or components as needed. Furthermore, monitoring the hydraulic fluid for quality and viscosity can help predict potential issues. Documenting maintenance activities aids in identifying trends over time and ensures that any recurring problems can be addressed promptly. Implementing these best practices will not only enhance the functionality of hydraulic control valves but also extend the lifespan of the entire system.